When most people think of strength and fitness, they imagine heavy dumbbells, bench presses, and high-tech gym machines. But here’s the truth: your own body is the most powerful piece of fitness equipment you’ll ever own. With the right moves, bodyweight exercises can be more effective than gym machines for fat loss, muscle gain, and functional strength.
Why? Because bodyweight training doesn’t just build muscles—it rewires your entire physiology. When you perform moves like push-ups, squats, or burpees, your body releases fat-burning hormones like epinephrine and norepinephrine, anabolic agents like growth hormone (GH) and testosterone, and powerful proteins called myokines, which regulate fat oxidation and reduce inflammation. Unlike machines, which isolate muscles, bodyweight workouts engage stabilizers, improve balance, and train your nervous system to coordinate real-world movements.
Let’s break down the most powerful bodyweight exercises, the science behind them, and why they sometimes outperform gym-based training.
Push-Ups: A Full-Body Hormone Booster
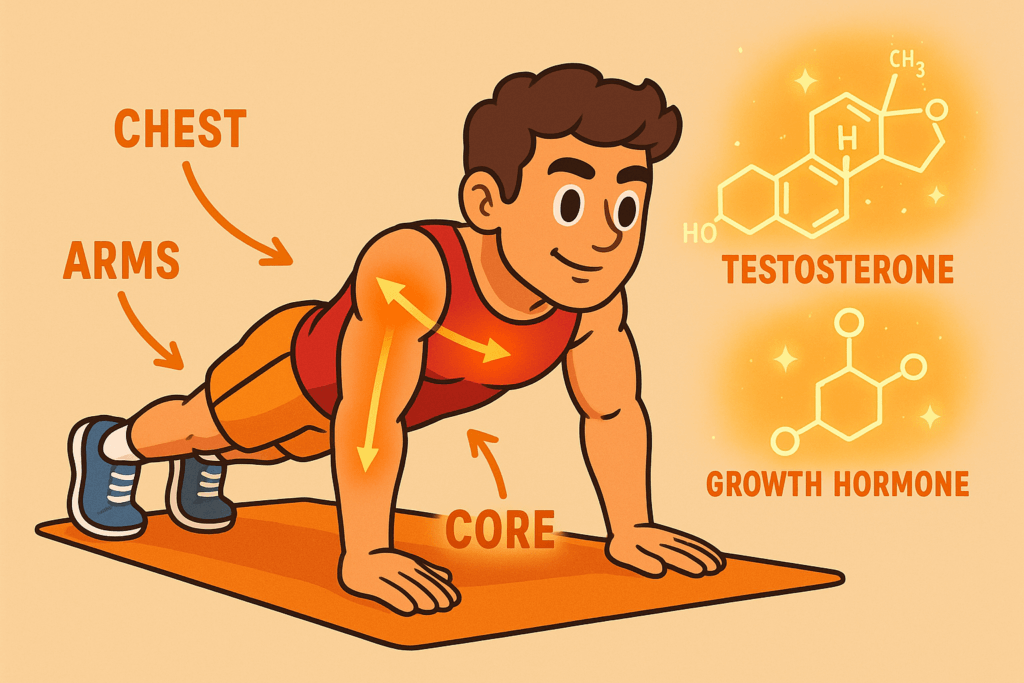
Push-ups may look simple, but they’re a compound movement that targets your chest, triceps, shoulders, and core.
- Hormonal Effect: Push-ups increase testosterone and growth hormone, essential for lean muscle gain and fat loss.
- Circulation: Repeated contractions improve blood flow and release nitric oxide, which dilates vessels and boosts oxygen delivery.
- Neurological Benefit: Push-ups activate stabilizers and proprioception, something machines often fail to do.
Advanced Variations: Archer push-ups, one-arm push-ups, explosive clap push-ups, weighted push-ups.
Why better than machines: Unlike a chest press machine, push-ups require total body tension and core engagement, making them a superior functional strength builder.
Squats: The Hormonal Powerhouse
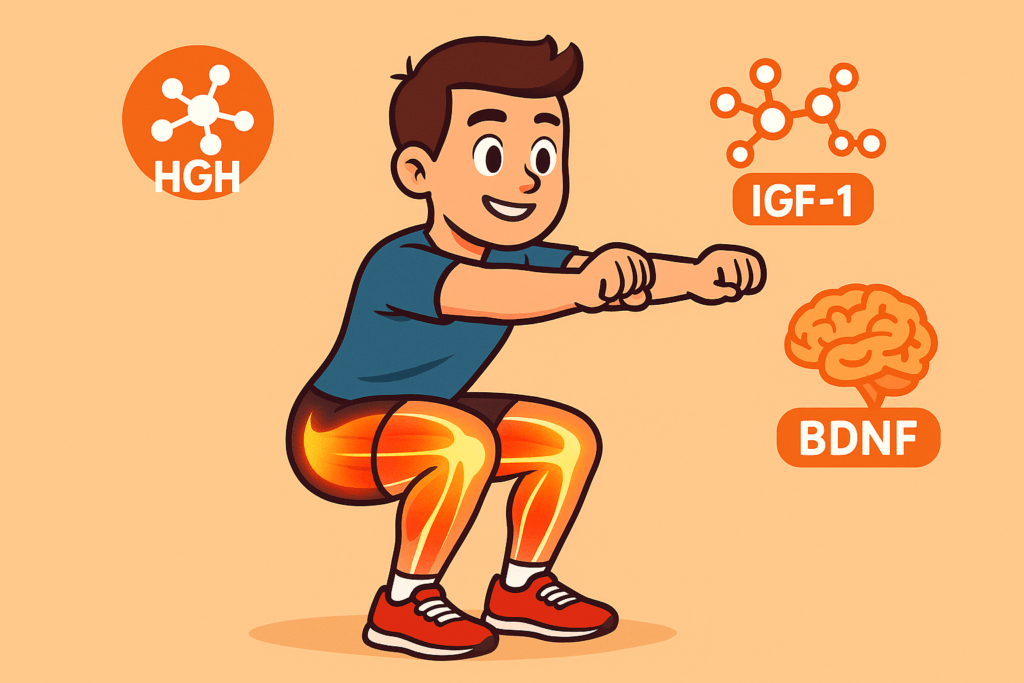
Squats are the king of lower-body exercises—and one of the best fat-burning moves overall.
- Hormonal Surge: Squats elevate testosterone, IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1), and growth hormone more than almost any other bodyweight exercise.
- Lactate Build-Up: High-rep squats create lactic acid, stimulating BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor), improving brain health and mood.
- Mobility Impact: Squats enhance hip, ankle, and lower back flexibility, reducing injury risk.
Advanced Variations: Jump squats, pistol squats, Bulgarian split squats, wall sits.
Why better than machines: Leg press machines isolate quads but neglect stabilizers and balance. Squats train real-life strength and movement efficiency.
Fitness Myths You Need to Stop Believing Right Now
Pull-Ups: The True Upper-Body Test
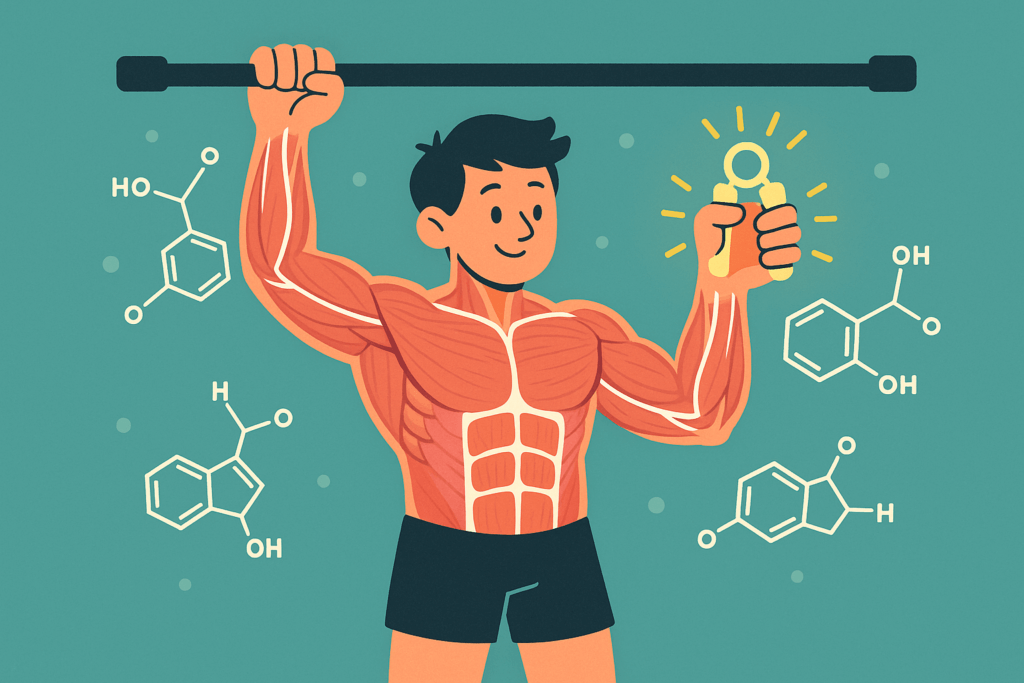
Pull-ups build raw strength in your back, arms, shoulders, and grip.
- Hormonal Impact: Stimulates testosterone and catecholamines (adrenaline/noradrenaline).
- Metabolic Boost: Pull-ups recruit multiple large muscles at once, burning calories efficiently.
- Longevity Link: Grip strength, developed heavily in pull-ups, is a predictor of overall health and lifespan.
Advanced Variations: Chin-ups, wide-grip pull-ups, muscle-ups, towel pull-ups for grip.
Why better than machines: Lat pulldown machines mimic pull-ups but don’t recruit stabilizers or challenge grip and core to the same degree.
Planks: Core Strength Beyond Crunches
Planks are an isometric hold that train your core as a functional unit.
- Hormonal Effect: Long planks reduce cortisol while increasing endorphins for stress relief.
- Neurological Training: Enhances motor control and stability across multiple muscle groups.
- Myokine Release: Static holds release muscle messengers like IL-6, which help regulate fat oxidation.
Advanced Variations: Side planks, plank reaches, plank jacks, weighted planks.
Why better than machines: Ab machines isolate muscles but don’t improve total-body core stability. Planks train the deep core needed for posture and injury prevention.
Burpees: The Fat-Burning Furnace
Burpees are a total-body move combining a push-up, squat, and jump.
- Hormonal Blast: Burpees spike epinephrine, norepinephrine, and growth hormone, accelerating fat burn.
- Afterburn Effect: EPOC (Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption) stays high, keeping metabolism elevated for hours.
- Mental Benefit: Builds resilience and mental toughness.
Advanced Variations: Burpee pull-ups, one-leg burpees, half-burpees for beginners.
Why better than machines: Treadmills and ellipticals provide cardio, but burpees add strength, coordination, and a full hormonal response in less time.
Dips: Chest and Triceps Without Machines
Dips strengthen chest, shoulders, and triceps using nothing but your body and parallel bars (or even a chair).
- Hormonal Trigger: Heavy stress on large muscle groups boosts testosterone.
- Functional Strength: Mimics natural pushing movements.
- Stabilizer Activation: Unlike triceps pushdowns, dips demand balance and full-body coordination.
Lunges: Balance, Mobility, and Power
Lunges are unilateral (single-leg) exercises that build strength, balance, and flexibility.
- Hormonal Effect: Stimulates growth hormone, improves insulin sensitivity.
- Neurological Benefit: Improves proprioception (balance awareness).
- Mobility: Stretches hip flexors and strengthens glutes simultaneously.
Advanced Variations: Jump lunges, walking lunges, reverse lunges, side lunges.
Why better than machines: Leg extension machines isolate one muscle, while lunges train movement patterns used in daily life.
The Science of Bodyweight vs Machines
Why bodyweight often outperforms machines:
- Functional Strength: Moves mimic real-world activity, not isolated machine patterns.
- Hormonal Response: More muscle recruitment → higher hormone release (GH, testosterone, myokines).
- Balance & Stability: Machines support you artificially; bodyweight exercises make your nervous system work harder.
- Scalability: Variations make bodyweight infinitely adaptable.
- Accessibility: No equipment or memberships needed.
Side Effects and Precautions
- Poor form in advanced moves can cause strain.
- Overtraining bodyweight HIIT without rest can spike cortisol.
- Beginners should progress gradually.
FAQs
1. Can bodyweight exercises replace gym workouts?
Yes. With progressive overload and intensity, they stimulate the same anabolic pathways as weights.
2. Which bodyweight exercise burns the most fat?
Burpees and jump squats, due to adrenaline spikes and afterburn effect.
3. Can women build strength with bodyweight moves?
Yes. They boost lean muscle and strengthen bones without bulky muscle gain.
4. Do push-ups and pull-ups increase testosterone?
Yes. Large compound bodyweight moves trigger testosterone and growth hormone release.
5. Are machines ever better?
Machines help beginners, rehab patients, or when isolating specific muscles—but they can’t match the total-body benefits of bodyweight exercises.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. We are not doctors. Always consult your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not rely on online content alone to make decisions about your health.
