When it comes to weight loss, there’s no shortage of diet plans and strategies. However, low-carb diets like the Atkins Diet and Keto Diet have gained significant popularity in recent years for their ability to help individuals shed weight efficiently. But how do these two diets stack up against each other? Which one offers the best results in terms of weight loss? This blog post will help you understand the key differences between the Atkins Diet and Keto, and help you choose the right approach for your weight loss journey.
Atkins Diet: A Proven Low-Carb Approach
The Atkins Diet is a low-carb, high-protein, and moderate-fat diet plan designed to promote fat burning by dramatically reducing carb intake. First introduced by Dr. Robert Atkins in the 1970s, it quickly became one of the most well-known low-carb diets worldwide. The key principle behind this diet is simple: by cutting carbs and replacing them with protein and fat, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it begins to burn fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Phases of the Atkins Diet:
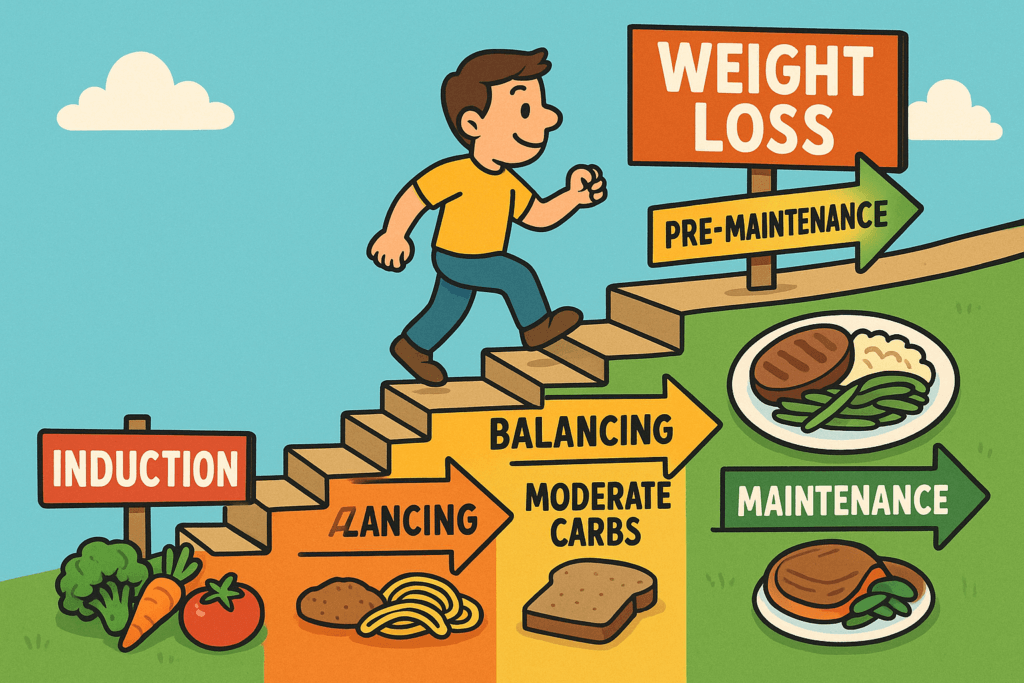
The Atkins Diet is divided into four phases. Each phase has a different approach to managing carbs, designed to help you gradually transition into a sustainable, long-term way of eating:
- Induction Phase: The most restrictive phase, where carbohydrate intake is limited to just 20 grams per day. This phase forces your body to begin burning fat for fuel.
- Balancing Phase: Here, you slowly start adding more carbs in the form of low-carb vegetables, nuts, and seeds. The goal is to find a balance where weight loss continues while still consuming enough carbs to feel satisfied.
- Pre-Maintenance Phase: This phase marks the transition toward maintaining your weight. As you approach your goal weight, carbs are added gradually to help maintain your new weight.
- Maintenance Phase: Once you reach your target weight, this phase helps you maintain your weight by keeping carb intake at a level that works for your body.
Benefits of the Atkins Diet:
- Rapid weight loss: The initial phases of the Atkins Diet can lead to quick weight loss due to the significant reduction in carbs and the body’s shift to burning fat.
- Improved blood sugar control: For those with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of diabetes, the Atkins Diet may help improve insulin sensitivity and stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Appetite control: The high-protein intake in the Atkins Diet helps reduce hunger and cravings, making it easier to stick to the plan.
Challenges of the Atkins Diet:
- Restrictive in the beginning: The induction phase can be difficult to stick with due to the drastic reduction in carbs.
- Potential nutrient deficiencies: If not carefully managed, the low-carb intake, especially in the early stages, may lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Digestive issues: The lack of fiber-rich foods in the initial stages may cause digestive problems like constipation for some individuals.
Keto Diet: A More Extreme Low-Carb Option
The Keto Diet has gained immense popularity over the past few years, particularly among those looking for a quick way to lose weight and improve mental clarity. Like the Atkins Diet, the Keto Diet is a low-carb diet designed to encourage your body to burn fat instead of carbs. However, the Keto Diet takes things a step further, recommending a very low-carb, high-fat eating plan to induce a metabolic state known as ketosis.
How Ketosis Works:
In ketosis, your body burns fat for energy rather than relying on glucose from carbohydrates. By significantly reducing carb intake and increasing fat consumption, your body shifts its fuel source from sugar to fat, leading to increased fat burning and weight loss. In order to stay in ketosis, carbs must be limited to around 20-50 grams per day.
Cucumber protein per 100g – Science Behind the Crunch
Macronutrient Breakdown on Keto:
- 70-80% of calories from fat
- 10-20% of calories from protein
- 5-10% of calories from carbohydrates
Benefits of the Keto Diet:
- Effective for rapid fat loss: Since the Keto Diet puts your body into ketosis, it accelerates fat burning and leads to quick weight loss, especially in the initial stages.
- Reduced hunger and cravings: A high-fat diet tends to be more filling than a high-carb one, helping to curb hunger and prevent overeating.
- Increased energy and mental clarity: Many people report feeling more energized and mentally clear when in ketosis, as the brain begins using ketones (produced from fat) as a fuel source.

Challenges of the Keto Diet:
- Keto flu: As the body adjusts to ketosis, some individuals experience symptoms known as the “Keto flu,” which can include headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
- Difficulty sustaining: Due to the strict carb limitations, the Keto Diet can be difficult for some people to sustain long-term.
- Potential health concerns: The high fat intake on the Keto Diet may not be suitable for people with certain health conditions, such as heart disease.
Atkins Diet vs Keto: Key Differences
While both diets promote fat burning by limiting carbohydrate intake, there are some notable differences in their approach. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Feature | Atkins Diet | Keto Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carb Intake | Gradually increases carbs through phases | Extremely low carb intake throughout the diet |
| Focus | High protein, moderate fat | Very high fat, moderate protein, very low carb |
| Phases | Structured with four distinct phases | No distinct phases, consistent low-carb focus |
| Weight Loss | Rapid initially, slows down over time | Rapid weight loss due to ketosis |
| Sustainability | Easier to maintain after induction phase | Challenging for many people to stick with long-term |
Which Diet is Better for Weight Loss?
The choice between Atkins Diet vs Keto ultimately depends on your preferences and long-term sustainability. If you want faster results and don’t mind restricting carbs dramatically, the Keto Diet may be the right choice for you. However, if you prefer a more gradual, structured approach with the option to reintroduce carbs over time, the Atkins Diet could be a better fit.
Remember, no matter which diet you choose, consistency is key. Both the Atkins and Keto diets are effective for weight loss, but only if you commit to the plan and make it a lifestyle change.
Focus Keyword: Atkins Diet vs Keto
When comparing Atkins Diet vs Keto, it’s clear that both have their strengths and challenges. Whether you choose the more gradual approach of Atkins or the strict, fat-burning focus of Keto, you can expect to see results with dedication and consistency.
But remember: always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new diet, especially one that restricts certain food groups, to ensure it’s a safe and suitable option for your health.
FAQs
1. What’s the main difference between the Atkins Diet and Keto?
The main difference is that the Atkins Diet has four phases, gradually increasing carb intake, while the Keto Diet focuses on keeping carbs extremely low to maintain ketosis.
2. How long should I stay on the Atkins or Keto diet?
It depends on your goals. Most people start seeing weight loss within the first few weeks. Both diets can be followed long-term, but it’s important to transition to a sustainable eating pattern afterward.
3. Can I drink alcohol on the Keto or Atkins diet?
Moderate alcohol consumption is allowed on both diets, but you must choose low-carb options. Beer and sugary cocktails should be avoided, while dry wines and spirits in moderation are usually okay.
4. Which diet is more effective for weight loss?
Both diets can be effective for weight loss. The Keto Diet may lead to quicker fat loss due to ketosis, while the Atkins Diet is more gradual, with better long-term sustainability for some.
5. Will I experience side effects on either diet?
Yes, both diets can cause side effects. The Keto Diet might lead to “Keto flu” when starting, and the Atkins Diet can cause digestive issues due to low fiber intake, especially in the early stages.
Disclaimer: We are not a doctor, please consult to your doctor fi you have any medical condition.
